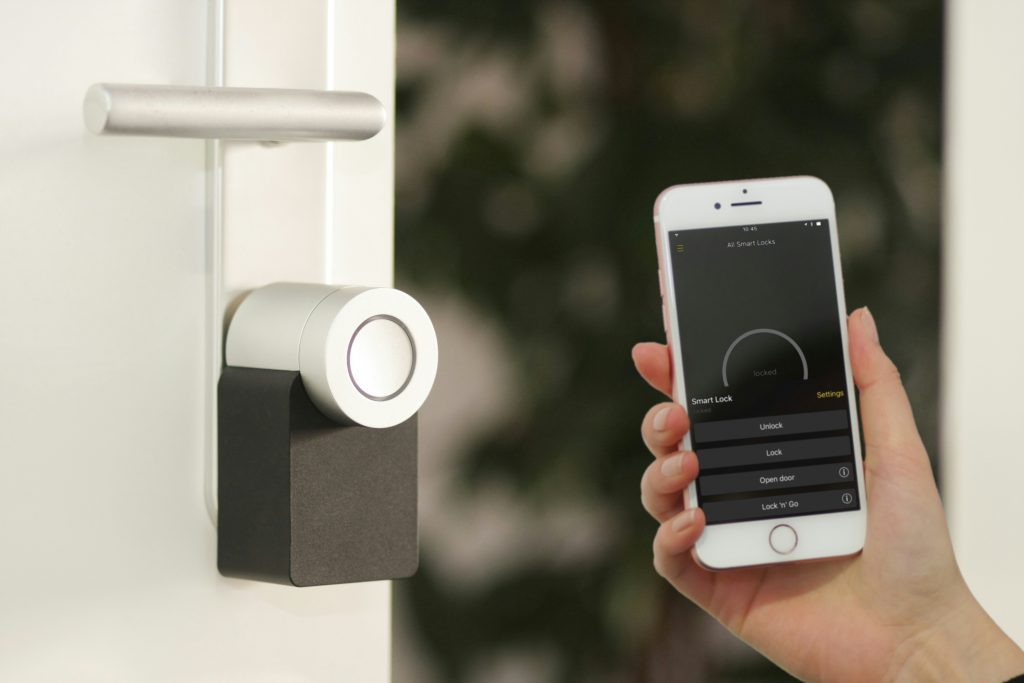
Smart homes are no longer just about voice assistants and automated lighting. A wave of new technologies—some already arriving on the consumer market, others on the horizon—is reshaping everyday life. From adaptive climate systems to privacy-first AI, here are five emerging smart home innovations that are practical, powerful, and poised to impact how you live in the years ahead.
Adaptive Climate & Energy Systems Powered by AI
Traditional home thermostats maintain fixed schedules or remote-control settings. The next generation uses machine learning to learn your rhythms, monitor weather forecasts, and manage energy efficiently without manual input.
These systems analyze occupant behavior—when people arrive, when rooms are used most—and dynamically adjust heating, cooling, ventilation, and even humidity. They optimize energy use while maintaining comfort. For example, if the system recognizes you leave home around 8 AM, it shifts climate control off during work hours and ramps up before your anticipated return.
Integration with solar generation and smart grid pricing means automated energy arbitrage: the system pre-cools or pre-heats the home during low-cost energy periods, storing thermal comfort while saving money. Over months, this adaptive approach reduces utility bills and carbon footprint—all while running transparently in the background.
Ambient AI for Routine Task Automation
Beyond voice commands, ambient AI refers to systems that passively “see” and assist—without requiring explicit user input. Sensors, cameras, and edge-based models operate locally to identify routine activities and offer help or suggestions.
Imagine walking into your kitchen and sensors detect you’re preparing coffee. The system quietly runs your preferred playlist, adjusts lighting to “morning mode,” and primes the kettle. Your coffee mug might be warmed on a smart coaster so it stays hot. These actions happen without penetration into your private conversations or cloud processing.
Ambient AI also aids safety: It detects if someone falls in the home (via motion sensors) and prompts a confirmation before alerting a trusted contact. Unlike full-blown surveillance, these systems work via pattern recognition at the edge without storing sensitive visual data.
Immersive Home Interfaces: Augmented Reality Control
Touchscreens and smart speakers are useful, but soon, control may move through your environment. Using augmented reality (AR) glasses or projection systems, you’ll see virtual controls overlaid on physical devices or rooms.
Want to adjust lighting? Simply gaze at the lamp, and a control panel will appear in AR, letting you dim or recolor the light instantly. Cooking dinner? A floating touchscreen near your stove displays recipes or timers. Walk into your bedroom, and AR overlays show room temperature and air quality or suggest relaxing soundscapes.
Voice, gesture, and gaze combine into an intuitive interface that reduces clutter—no apps, no remotes, no scrolling. These ambient overlays also maintain a clean aesthetic: your smart home remains visually minimal while delivering powerful interactivity when you look at it.
Privacy-First Smart Home Architecture
As smart homes get smarter, concerns about data privacy intensify. The next wave of systems embraces distributed, local-first architecture: on-device processing, encrypted communication, and minimal external data sharing.
Imagine a system where voice recognition, activity patterns, and personalization models all reside within home hardware—not in a cloud server. Occupant profiles, preferences, and analytics remain encrypted behind your router or near your central hub. Firmware updates may come via secure mesh networks rather than the public Internet.
These designs are not merely theoretical: upcoming smart home standards emphasize interoperable local networks, user-owned storage, and consent-based external sharing. The result: you enjoy responsive, machine learning–driven home experiences while retaining full control over your data.
Biometric & Context-Aware Personalization
Imagine your home responding uniquely to each person as they enter. This mindset underpins biometric and context-aware personalization: systems adapt lighting, HVAC, content suggestions, and even scent within minutes of recognizing an occupant.
Face recognition, wearable tag signals, or device proximity trigger the system to switch profiles—your temperature, healthy snack reminder, or preferred smart speaker settings. When siblings, guests, or relatives move through the house, everything resets to neutral before their profile is engaged.
These features extend to contextual triggers: workout completion cues a cooling cycle and hydration alert; returning home triggers relaxing music and warm lighting; entering the kitchen suggests healthy recipes if it’s nearly lunchtime.
Importantly, this advanced personalization works because it’s mapped to context, not recorded behavior—the system adapts while keeping baseline conditions and transitions secure and transient.
Implementation Tips for Homeowners and Builders
- Start Small, Expand Over Time
Begin with one AI climate device or ambient sensor. Let your home evolve rather than trying to install everything at once. Over time, new devices will integrate using common standards. - Choose Edge-Based Platforms
Prioritize platforms and devices that support local control and encrypted communication—edge-first systems offer more resilience and better privacy. - Plan for Interoperability
Look for devices that support open standards (Matter, HomeKit, Thread, Zigbee, OpenXR). These reduce vendor lock-in and ensure you can mix and match modern technology. - Avoid Data Lock-In
Opt for devices that allow you to control your own data or delete your personal profiles easily. Prefer systems that let you disable cloud syncing without losing smart features. - Test Behavior and Automations Gradually
Set automations with small triggers—light transitions, temperature adjustments—and gradually refine them over weeks. Let your system learn and adapt; don’t program it manually all at once.
Why It Matters: The Real-life Benefits
Implementing these technologies delivers measurable improvements:
- Energy savings from adaptive HVAC can range from 15–30%.
- Reduced decision fatigue, with routine elements automated—so you spend less mental energy on simple tasks.
- Enhanced personal comfort, with climate and ambiance tailored automatically to each occupant.
- Improved safety and peace of mind, via context-aware alerts and ambient monitoring.
- Long-term data sovereignty ensures your daily patterns and preferences remain secure.
Ultimately, these technologies transform a house into a responsive, comfortable, efficient, and privacy-aware environment.
Conclusion: A Smarter, Kinder Home of Tomorrow
The smart home revolution is shifting: from gimmicks to meaningful daily intelligence, from cloud risk to local resilience, and from one-size-fits-all to individually tuned environments. Emerging technologies—adaptive climate control, ambient AI, AR interfaces, privacy-first architecture, and biometric personalization—are creating homes that intuitively support human well-being.
At Chemniverse, our passion is exploring how science and systems intersect to create better human experiences. These technologies are not just futuristic—they’re practical, and you can start integrating them now with intentional, modular upgrades.